Cloning Objects
It's often faster to create a duplicate of an object than to bring in an entirely new primitive. Sometimes this is because you literally want a copy of an edit or a model somewhere else in your scene. Other times it's to more easily place a new edit adjacent to an existing one with a quick paste. And sometimes you'll be making use of linked models for mirroring an entire form or to quickly fill the scene with like-objects.
Copying and Pasting Models
The duo of copy (CRTL/CMD + C) and paste (CTRL/CMD + V) work as you might expect, placing an exact copy of a model or an edit directly on top of the source. You can then adjust the copy to your liking.
This new model will appear in the organizer as a separate object which, when changed, has no effect on the model from which it was copied.
Linked Models
Similarly, you can use the keyboard shortcut CTRL/CMD + D to create a duplicate of the selected model on top of the selected model. This too will appear as a separate model in the organizer and can be moved, rotated or scale independent of the source model.
However unlike copy/paste, this creates a linked model. You can identify linked models by the new button above their properties.

This newly created model is now linked to the model from which it was copied. It will inherit any changes made to the original model or that models internal edits.
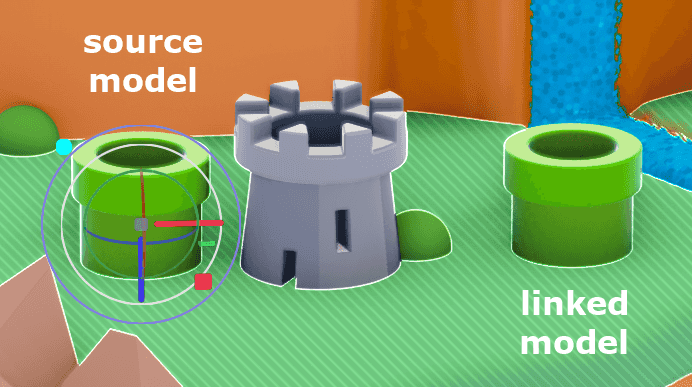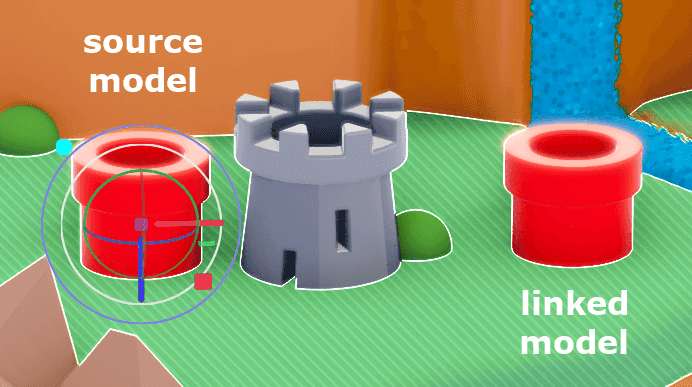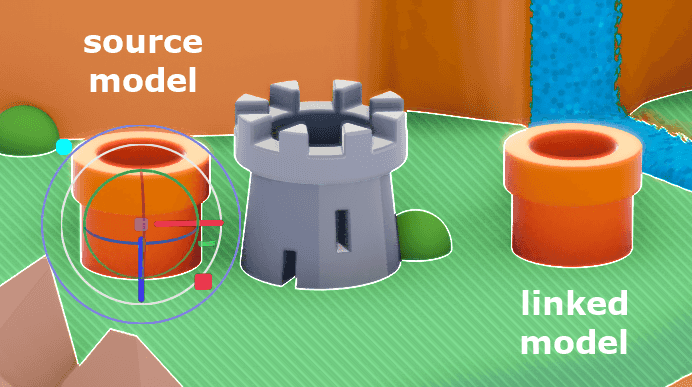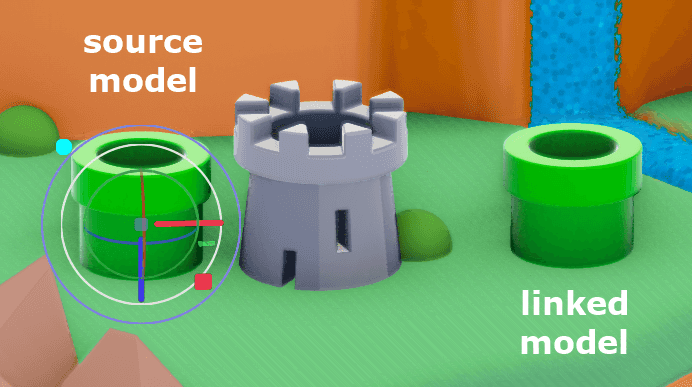
When unlinked, a model will retain the last state it was in but will no longer inherit changes from the original source model.
Tip
Cloned models take up relatively low memory (almost none) compared to unique models or duplicated models that have been simply copied and pasted. So besides the benefits described above, linked models have the added benefit of keeping your memory footprint low.
Clone Stamp Tool
Linked models can also be created with the clone stamp tool. This is commonly used to quickly create a bunch of scene decoration from a single model.
From the Sculpt Tab you can select a model and then click the clone stamp tool to create a stamp.

However it's much more efficient to use the keyboard shortcut C. This will place a linked duplicate of the selected model on your cursor, which you can then place with a single click. In this way you can rapidly create linked duplicates to decorate a scene. This technique is often paired with the surface snap setting, which is covered in this article.
Mirror Duplicate

The mirror duplicate tool will create a mirror image of the selected model. A model created in this way is NOT linked.
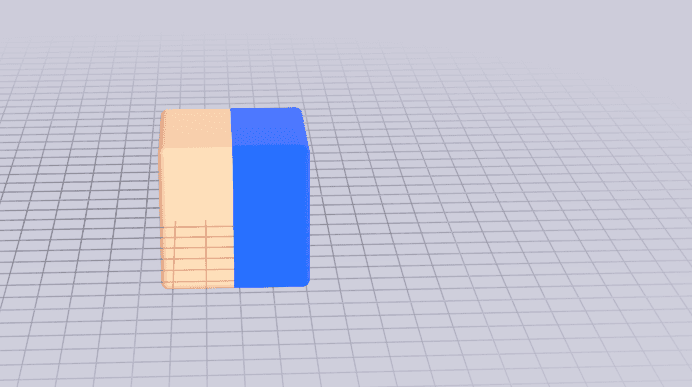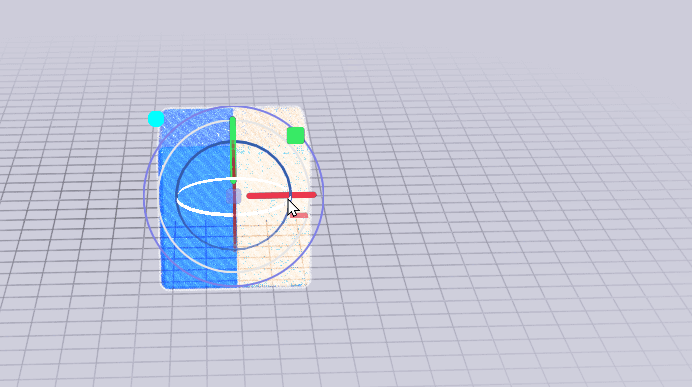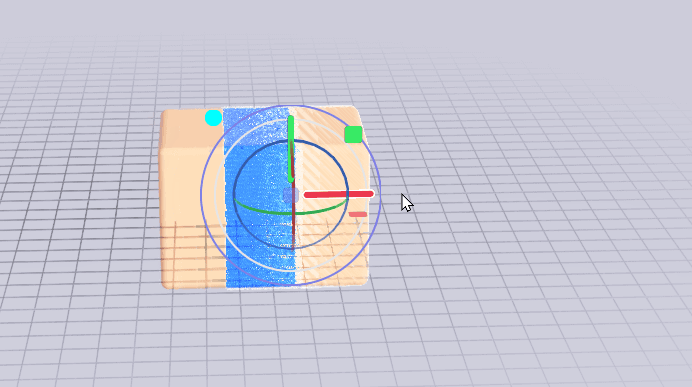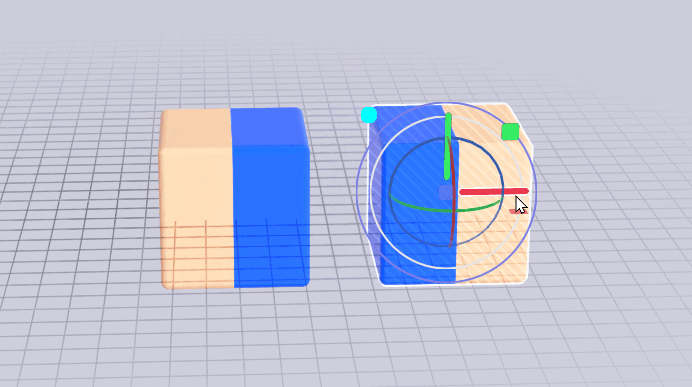
If you'd like to mirror a model that is also linked to a source model, you can use a joint.
Tip
You can also use the mirror modifier mode discussed in Working with Edits, but sometimes it's impossible or impractical to mirror something inside of a model. An example would be if you wanted to have the same arm on both sides of a character but position them differently. For that you'll need a joint.
Mirroring with Joints
Joints have many uses that span from grouping models under an invisible parent transform to rigging characters. In this article we're going to focus on using them to mirror a linked model.
From the Stage Tab, select the model(s) you'd like to mirror and then click the + joint tool. This will nest any selected models under a single joint.
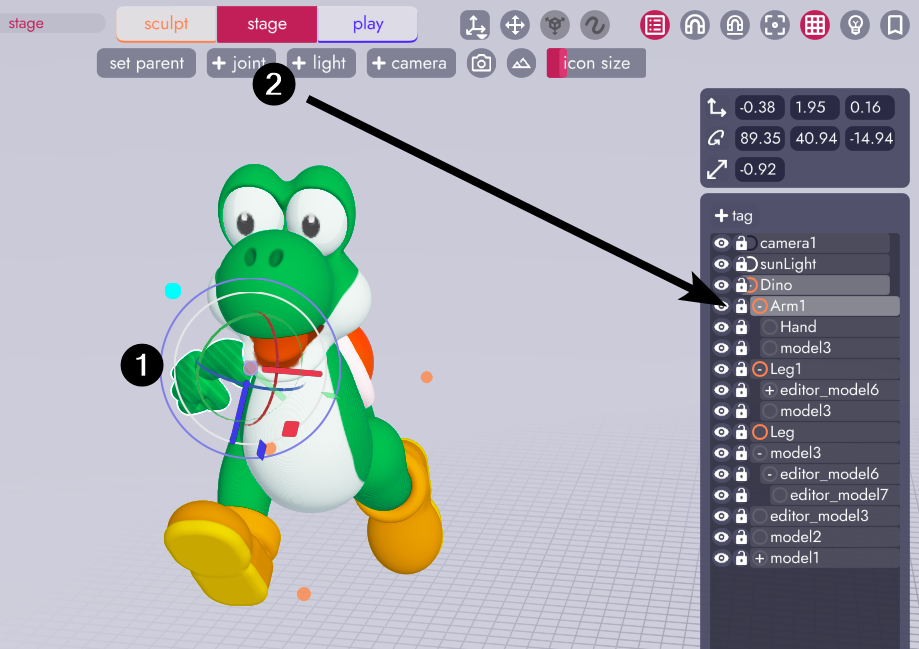
Then back in the Sculpt Tab, use CTRL/CMD + D to duplicate the model (to create a linked model) and position it roughly where you'd like the new model to be. You now have two arms both nested under their own joint, linked to the original model.
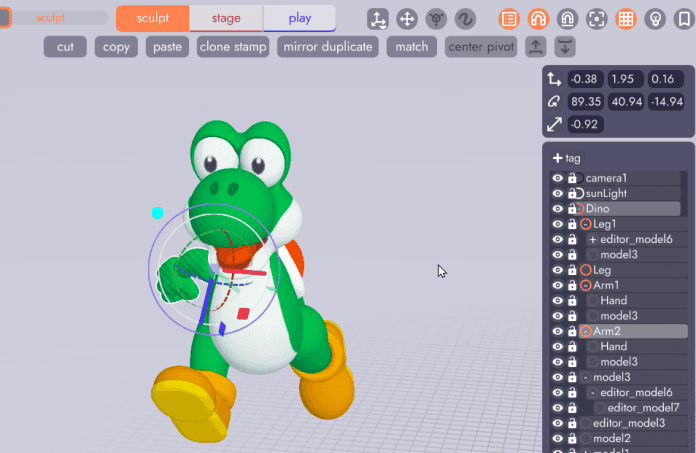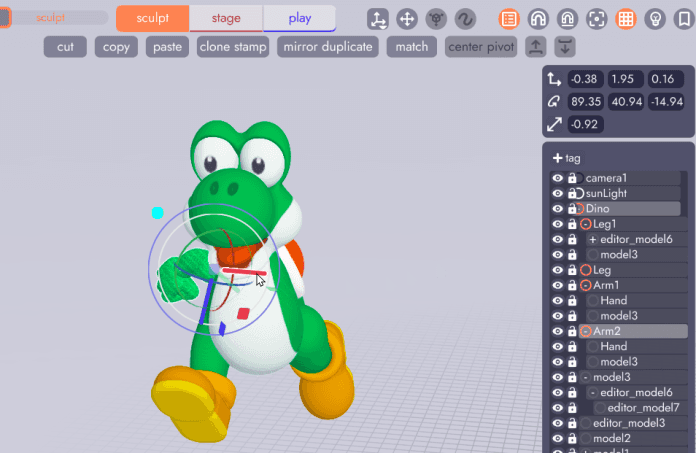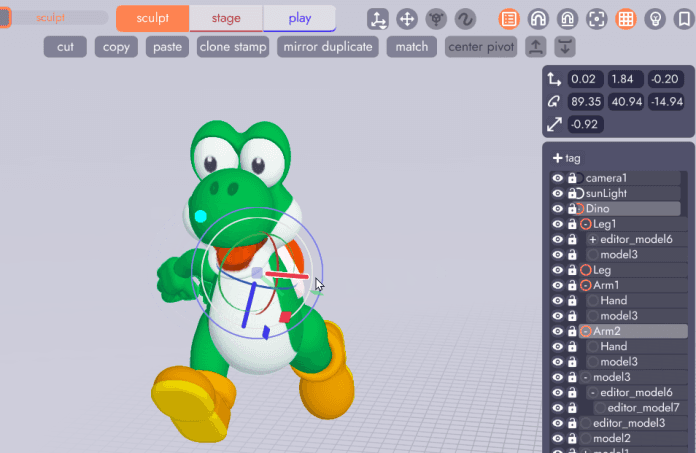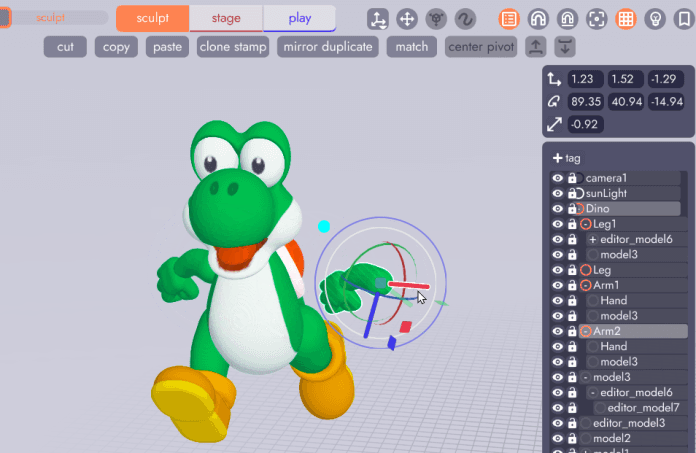
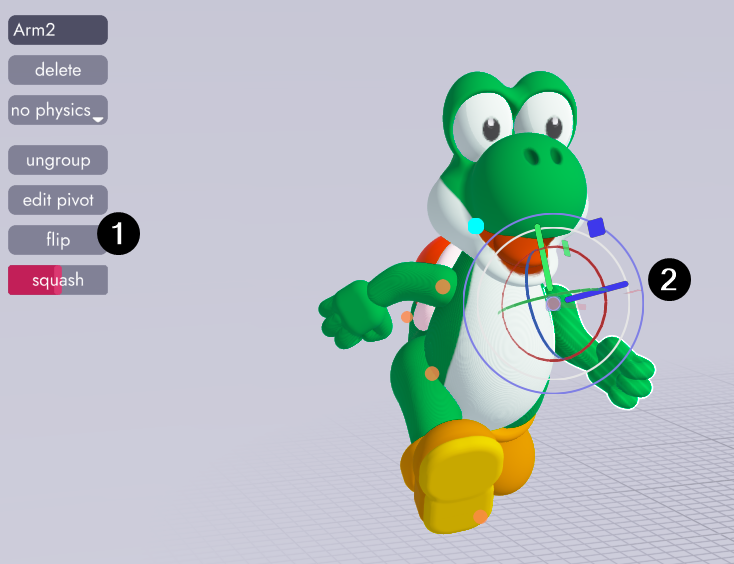
Returning to the Stage Tab select the new arm, click the flip tool, then rotate the arm into the correct position. Arm 2 is now linked to the original, meaning it will inherit changes like color or newly modeled fingers, but is mirrored on the Y axis and can be rotated independently!
What Next?
You may have noticed that joints have an extra property called squash that models do not. That property comes in handy when animating models, which you can learn more about here.
